Description
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-colors/
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
- Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each row. - Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each column. - Each of the the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each of the 93x3sub-boxes of the grid.
Empty cells are indicated by the character '.'.
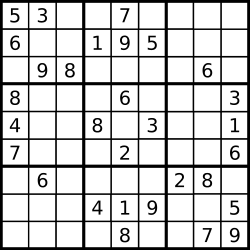
A sudoku puzzle…
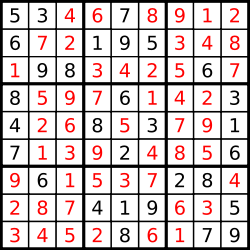
…and its solution numbers marked in red.
Note:
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'. - You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
- The given board size is always
9x9.
Explanation
backtracking
Python Solution
class Solution:
def solveSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
board_assignment = self.get_board_assignment(board)
self.backtracking_helper(board, 0, board_assignment)
def backtracking_helper(self, board2d, index, board_assignment):
if index == 81:
return True
row_index = index // 9
column_index = index % 9
if board2d[row_index][column_index] != '.':
return self.backtracking_helper(board2d, index + 1, board_assignment)
unassigned_variables = [i for i in range(1, 10)]
for value in unassigned_variables:
value = str(value)
if not self.is_valid_assignment(row_index, column_index, value, board_assignment):
continue
self.add_value_to_assignment(board2d, board_assignment, column_index, value, row_index)
if self.backtracking_helper(board2d, index + 1, board_assignment):
return True
self.remove_value_from_assignment(board2d, board_assignment, column_index, value, row_index)
return False
def remove_value_from_assignment(self, board2d, board_assignment, column_index, value, row_index):
board2d[row_index][column_index] = '.'
del board_assignment['columns'][column_index][value]
del board_assignment['rows'][row_index][value]
del board_assignment['boxes'][row_index // 3 * 3 + column_index // 3][value]
def add_value_to_assignment(self, board2d, board_assignment, column_index, value, row_index):
board2d[row_index][column_index] = value
board_assignment['rows'][row_index][value] = True
board_assignment['columns'][column_index][value] = True
board_assignment['boxes'][row_index // 3 * 3 + column_index // 3][value] = True
def is_valid_assignment(self, row_index, column_index, digit, board_assignment):
if digit in board_assignment['rows'][row_index]:
return False
if digit in board_assignment['columns'][column_index]:
return False
if digit in board_assignment['boxes'][row_index // 3 * 3 + column_index // 3]:
return False
return True
def get_board_assignment(self, board2d):
rows = [{} for i in range(0, 9)]
columns = [{} for j in range(0, 9)]
boxes = [{} for k in range(0, 9)]
for i in range(0, len(board2d)):
for j in range(0, len(board2d[0])):
value = board2d[i][j]
box_index = (i // 3) * 3 + j // 3
if value != '.':
rows[i][value] = True
columns[j][value] = True
boxes[box_index][value] = True
board_assignment = {'rows': rows, 'columns': columns, 'boxes': boxes}
return board_assignment- Time complexity: O((9!)^9).
- Space complexity: the board size is fixed, and the space is used to store board, rows, columns and boxes structures, each contains 81 elements
I found this solution very popular and helpful:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H5i2ugoZLbg&ab_channel=EricProgramming